Patcher Use Cases
Some examples of scenarios where Patcher can be useful

# This is an example Patch file to update from
# Terraform 0.13 to 0.14
code_transformations:
# Update Terratest and Go modules to the latest
- run_go_mod_tidy
# Add .terraform.lock.hcl to .gitignore
- add_lock_to_gitignore
# Update all Gruntwork modules
- update_module_versions
# Add required_providers block
- replace_provider_versions_with_required_providers
custom_scripts:
# Run Terraform format
- terraform_fmt
# Run Terraform validate
- terraform_validate
Example #1
Update to Terraform 1.0
- Use Patcher to update your Terraform code from an older version (e.g. 0.11) all the way up to the latest version (e.g. 1.0) automatically.
- Patcher does this using Patch Files, which transform code automatically (e.g. switching from HCL1 to HCL2 syntax or updating
sourceURLs to compatible module versions) and open pull requests with the results. - You can use off-the-shelf Patch Files created by Gruntwork (e.g. we offer Terraform upgrade patches such as
tf-13-to-14.patch,tf-14-to-15.patch, etc) or create your own Patch Files!
Example #2
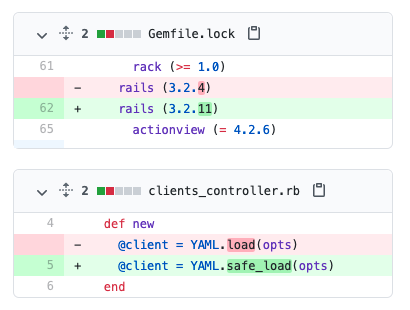
Patch a vulnerability in Rails
- Ruby on Rails has had several severe vulnerabilities with YAML parsing (e.g., CVE-2013-0156) that allowed remote attackers to execute arbitrary code, conduct SQL injection attacks, or bypass authentication.
- You can use Patcher to automatically update your Rails app to fix this vulnerability.
- Patcher can not only update you to the new version of Ruby on Rails, but also make the necessary changes to your app code to ensure the vulnerability is fully fixed.
# This is an example Patch file to update services
# using security.jar with new parameters
code_transformations:
# Update all users to the new auth method
- update_to_new_auth_method
custom_scripts:
# Error out on improper auth method usage
- detect_deprecated_auth_method
Example #3
Keep all microservices patched with the latest internal Java library
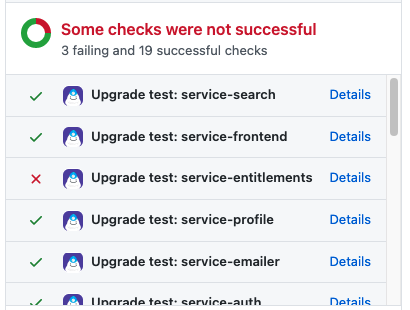
- You make a change to
security.jar, a library used by many microservices within your company, and open a pull request. - Patcher automatically finds all those services and runs their tests with your updates (Upgrade Tests), so you know if any of your changes were breaking.
- If you did make breaking changes, you can create a Patch File to patch those services, and Patcher will run Upgrade Tests with your updated code and Patch File.
- When you release a new version of
security.jar, Patcher will automatically update each service to use it, including running your Patch File.